
This article contains two parts.
Introduction In the context of new and changing regulations, increasing cybersecurity risks, and evolving consumer expectations, ensuring data privacy has become a top priority for consumers. To help companies understand the current situation, we will explore a trend in e-commerce: data privacy and transparency, which remain of utmost importance to consumers.
In today’s e-commerce world, where billions of transactions are made daily, trust has become one of the most valuable assets. The statistics speak for themselves: 81% of consumers prefer to shop from vendors they trust. While you work hard to earn trust in your product and brand, companies distributing cheap knock-offs significantly undermine it. Such actions not only deprive you of deserved profits but also jeopardize your reputation as a reliable seller. E-commerce customers indeed want an incredible, personalized, and flawless experience but not at the expense of questionable data practices. As companies now rely on new artificial intelligence capabilities and hyper-personalization strategies, it is crucial that maintaining customer trust remains their top priority.
Data Privacy and Transparency

Data privacy means protecting personal information from unauthorized access. This concept includes measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. Gartner predicts that by the end of 2024, 75% of the world’s population will have personal data covered by privacy regulations. This means that companies caught violating these requirements will face huge fines and legal consequences. Beyond financial risks of regulatory violations, brands that undermine customer trust, especially when it comes to their personal data, risk losing their business for life (not to mention the negative reviews they will receive).
Transparency is about companies being open about how they collect, use, and share personal data. It is important for companies to clearly inform consumers about their data policies. In today’s world, where consumers are becoming more informed and demanding, corporate transparency is a key factor influencing purchasing decisions. Transparency not only helps build trust and loyalty among customers but also strengthens the brand’s reputation in the market. Transparency starts with openness about the product: where it comes from, the conditions of its production, its environmental impact, and the social responsibility of the producers. Studies show that consumers prefer to buy from companies that do not hide this information. For example, according to Nielsen, over 73% of consumers are willing to pay more for products that provide complete transparency. 94% of companies claim that their customers would not buy from them if they did not adequately protect their data (Cisco).
Legislative Aspects

As consumers become more aware of the importance of data privacy, more people are taking significant steps to protect it. These statistics highlight the crucial role of data privacy in shaping consumer perceptions and behavior. 71% of consumers say they would stop doing business with a company if it misuses their confidential data (McKinsey). Nearly 68% of consumers worldwide said they are somewhat or very concerned about their online privacy (International Association of Privacy Professionals). Information security has become one of the most complex areas of law. The reasons for this development are numerous EU directives and national laws in most countries. The main principle of information security is the initial prohibition of information use. Thus, storage, transmission, or alteration of information is initially prohibited. This rule does not apply to the use of information that is allowed by law or the interested party. • Over 160 privacy laws have been enacted worldwide (ISACA). Every company must comply with data protection regulations, regardless of its number of employees and field of activity. However, the size and number of employees of your company affect the data protection procedures within your company. • With the adoption of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), for the first time across Europe, there was an obligation to appoint data protection officers for companies and public authorities. According to the employee data protection legislation, companies with at least 10 employees must appoint a data protection officer. Also, the GDPR establishes general requirements, including the right to be forgotten, the right to access data, and consent requirements for data processing. • By 2024, more than 120 countries will have international data privacy laws (World Population Review). In recent years, government oversight of companies’ information security and compliance with data protection laws has increased significantly, with fines and criminal liability being actively applied.
Data Leaks or Information Misuse

Examples pointing to recent scandals or issues related to data leaks or misuse that highlight the relevance of this topic:
Examples of Consumer Data Privacy Violations
- Facebook (Meta Platforms): In 2019, the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) imposed a record $5 billion fine on Facebook for privacy violations. The company was accused of misleading users about their ability to control their data and sharing personal information with third parties without their knowledge. In addition to the fine, Facebook was required to implement new measures to ensure transparency and accountability in data privacy matters (Federal Trade Commission).
- Lenovo and Vizio: In 2018, Lenovo and Vizio were also at the center of privacy scandals. Lenovo installed software on its computers that sent user data to third parties without their knowledge. Vizio collected data on viewing habits on its “smart” TVs and sold it without user notification and consent. Both cases led to major settlements with the FTC, resulting in the companies being required to change their practices and implement data protection programs (SGR Law).
- VTech: The toy manufacturer VTech was fined $650,000 for collecting personal information from children without parental consent. This was the first FTC case related to children’s data security, leading the company to improve its data protection measures and undergo regular audits for 20 years (SGR Law).
- GDPR and Meta: In 2023, Meta (Facebook) received the largest fine in GDPR history – €1.2 billion for transferring European user data to the U.S. without adequate data protection mechanisms. This set an important precedent in data protection regulation and showed that GDPR violations can lead to significant financial consequences (Data Privacy Manager).
- Facebook (Meta Platforms): In 2019, the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) imposed a record $5 billion fine on Facebook for privacy violations. The company was accused of misleading users about their ability to control their data and sharing personal information with third parties without their knowledge. In addition to the fine, Facebook was required to implement new measures to ensure transparency and accountability in data privacy matters (Federal Trade Commission).
- Lenovo and Vizio: In 2018, Lenovo and Vizio were also at the center of privacy scandals. Lenovo installed software on its computers that sent user data to third parties without their knowledge. Vizio collected data on viewing habits on its “smart” TVs and sold it without user notification and consent. Both cases led to major settlements with the FTC, resulting in the companies being required to change their practices and implement data protection programs (SGR Law).
- VTech: The toy manufacturer VTech was fined $650,000 for collecting personal information from children without parental consent. This was the first FTC case related to children’s data security, leading the company to improve its data protection measures and undergo regular audits for 20 years (SGR Law).
- GDPR and Meta: In 2023, Meta (Facebook) received the largest fine in GDPR history – €1.2 billion for transferring European user data to the U.S. without adequate data protection mechanisms. This set an important precedent in data protection regulation and showed that GDPR violations can lead to significant financial consequences (Data Privacy Manager).
- Facebook (Meta Platforms): In 2019, the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) imposed a record $5 billion fine on Facebook for privacy violations. The company was accused of misleading users about their ability to control their data and sharing personal information with third parties without their knowledge. In addition to the fine, Facebook was required to implement new measures to ensure transparency and accountability in data privacy matters (Federal Trade Commission).
- Lenovo and Vizio: In 2018, Lenovo and Vizio were also at the center of privacy scandals. Lenovo installed software on its computers that sent user data to third parties without their knowledge. Vizio collected data on viewing habits on its “smart” TVs and sold it without user notification and consent. Both cases led to major settlements with the FTC, resulting in the companies being required to change their practices and implement data protection programs (SGR Law).
- VTech: The toy manufacturer VTech was fined $650,000 for collecting personal information from children without parental consent. This was the first FTC case related to children’s data security, leading the company to improve its data protection measures and undergo regular audits for 20 years (SGR Law).
- GDPR and Meta: In 2023, Meta (Facebook) received the largest fine in GDPR history – €1.2 billion for transferring European user data to the U.S. without adequate data protection mechanisms. This set an important precedent in data protection regulation and showed that GDPR violations can lead to significant financial consequences (Data Privacy Manager).
These examples demonstrate that companies violating consumer data privacy can face serious financial penalties and requirements to change their practices. For consumers, this often means a leak of personal information and potential risks associated with its misuse. The frequency and severity of cybersecurity incidents and data breaches are increasing worldwide, making discussions about customer data privacy more relevant than ever. These statistics highlight the relevance and impact of violations on both consumers and companies.
Examples of Transparency Violations in Various Industries
- Healthcare: Pricing transparency issues for medical services remain relevant in the U.S. Studies show that prices for the same medical services can vary by 40-50% within a single region. This makes it difficult for patients to compare and choose the most suitable options, leading to significant financial consequences. For example, an employer in Pennsylvania was able to save up to 43% on healthcare costs by using price transparency data (McKinsey & Company) (American Council on Science and Health).
- Fashion: In the fashion industry, the transparency issue concerns supply chains and working conditions. Consumers increasingly demand information on how and where products are made. Brands like Arket and Reformation have implemented radical transparency practices, providing detailed information on production processes and their environmental impact. This helps restore consumer trust and meet their expectations regarding sustainability and ethical production (McKinsey & Company).
- Automotive Industry: One of the most well-known examples of a lack of transparency is the Volkswagen emissions scandal. The company used software to cheat emissions tests, leading to significant reputational and financial losses. This case underscores the importance of honesty and transparency in corporate practices, as deception can severely damage consumer trust and lead to legal consequences (Ohio State Pressbooks).
These examples highlight that a lack of transparency can have serious consequences for companies, including loss of trust, legal sanctions, and financial losses. Consumers may suffer from inflated prices, deception, and unethical production. Therefore, transparency becomes an important aspect of building sustainable and trustworthy relationships between businesses and customers. Meanwhile, according to statistics, only 29% of consumers worldwide stated that they find it easy to understand how well a company protects their personal data (International Association of Privacy Professionals). 72% of Americans believe that government regulation of what can be done with personal data needs to be strengthened (Pew Research Center).
Statistical Data on Spending and Software for Ensuring Data Privacy
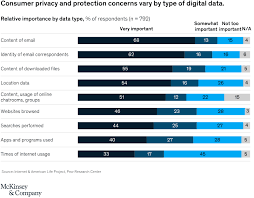
Over the past five years, total spending on data privacy has more than doubled (Cisco). Gartner predicts that by the end of 2024, the average annual budget for data privacy in large companies will exceed $2.5 million (Gartner).
80% of companies report increased customer loyalty and trust as a result of investments in data privacy. 78% report increased operational efficiency, flexibility, and innovation (Cisco). 5% of companies state that the benefits of investments in data privacy exceed the costs, with the average company receiving a 1.6x return on their privacy investments. 30% of organizations estimate a twofold return on investment in data privacy (Cisco). For every dollar spent on privacy, the average company receives $2.70 in accompanying benefits (Cisco). Nearly 93% of companies reported that privacy is among the top ten organizational risks, with 36% placing it in the top five (International Association of Privacy Professionals).
A survey of privacy professionals conducted by the International Association of Privacy Professionals identified the biggest risks to data privacy as:
- Data leaks
- Inappropriate third-party data processing
- Ineffective privacy by design
- Improper management of personal data
- Inadequate privacy training for employees
71% of employees worldwide admit to sharing confidential and business-critical data through instant messaging and collaboration tools. This data includes (Veritas):
- Customer information: 13%
- HR details: 10%
- Contracts: 10%
- Business plans: 10%
Diving into the field of data privacy software, statistics show how technological solutions impact data protection and compliance. The global market for data privacy software is projected to grow from $2.76 billion in 2023 to $30.31 billion by 2030, with an average annual growth rate of 40.9% (Fortune Business Insights). The adoption of data privacy technologies is expected to increase by 46% over the next three years (Zipdo).
Gartner predicts that by 2025, 60% of large companies will use at least one privacy-enhancing computation (PEC) method in analytics, business intelligence, and/or cloud computing to protect data in use (Gartner). Companies with fully deployed artificial intelligence and security automation report that the average cost of a data breach is $3.60 million—$1.76 million less than the losses in companies that did not use AI and automation security capabilities. This represents a 39.3% difference in the average cost of breaches (IBM).
To be continued in Part 2.



